Scientific Evidence

Consensus and guidelines on phytosterols in lipid management
More than 200 studies confirm the effectiveness of phytosterols in lowering cholesterol levels.
According to several international medical associations, a daily consumption of 2 grams of phytosterols is recommended to achieve this goal.



Cardiosmile Pivotal Trials
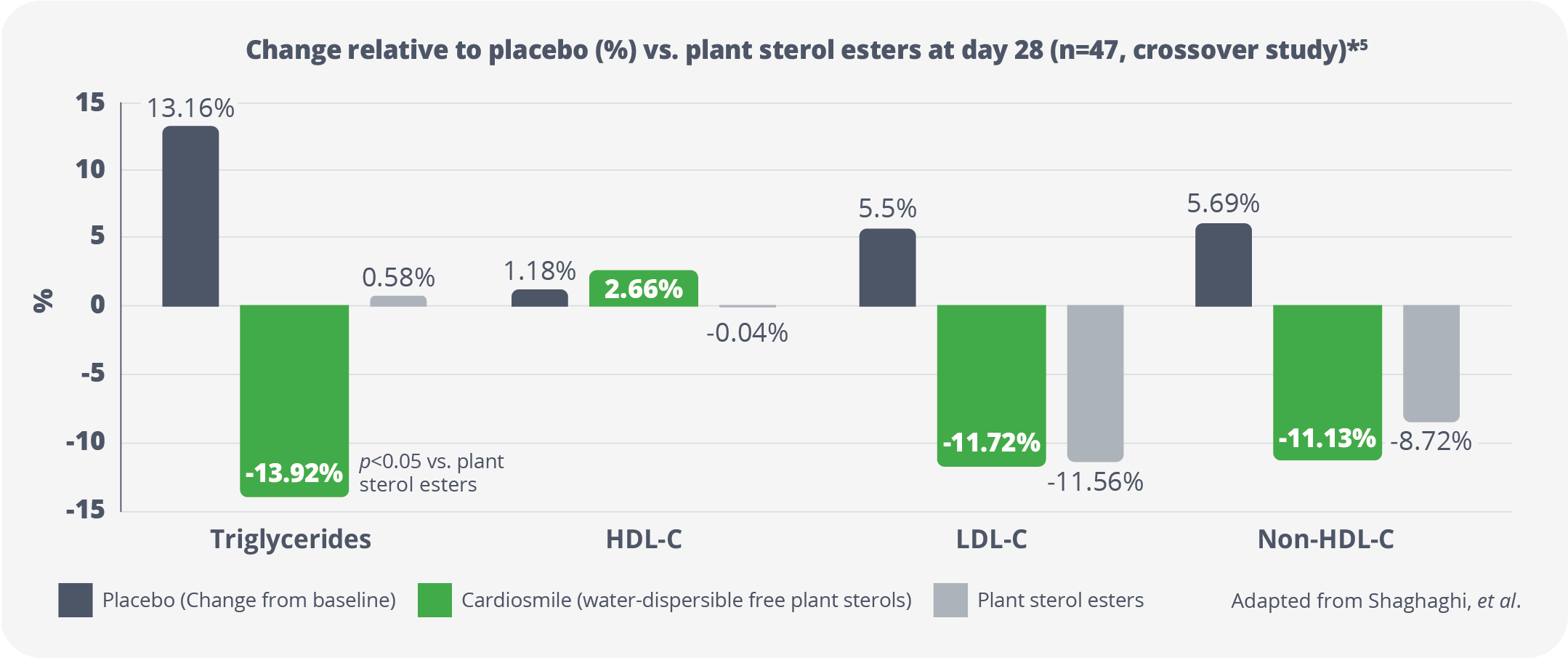
Efficacy results from Shaghaghi, et al.
A Canadian clinical study
After 28 days of consumption, Cardiosmile :
Supplementation of Cardiosmile and PS-ester did not adversely influence fat soluble vitamin or carotenoid levels before or after adjustment for LDL-C levels, compared to control.1
Cardiosmile and PS-ester favorably modified blood lipid profiles without altering plasma liver enzymes or CRP concentrations.1
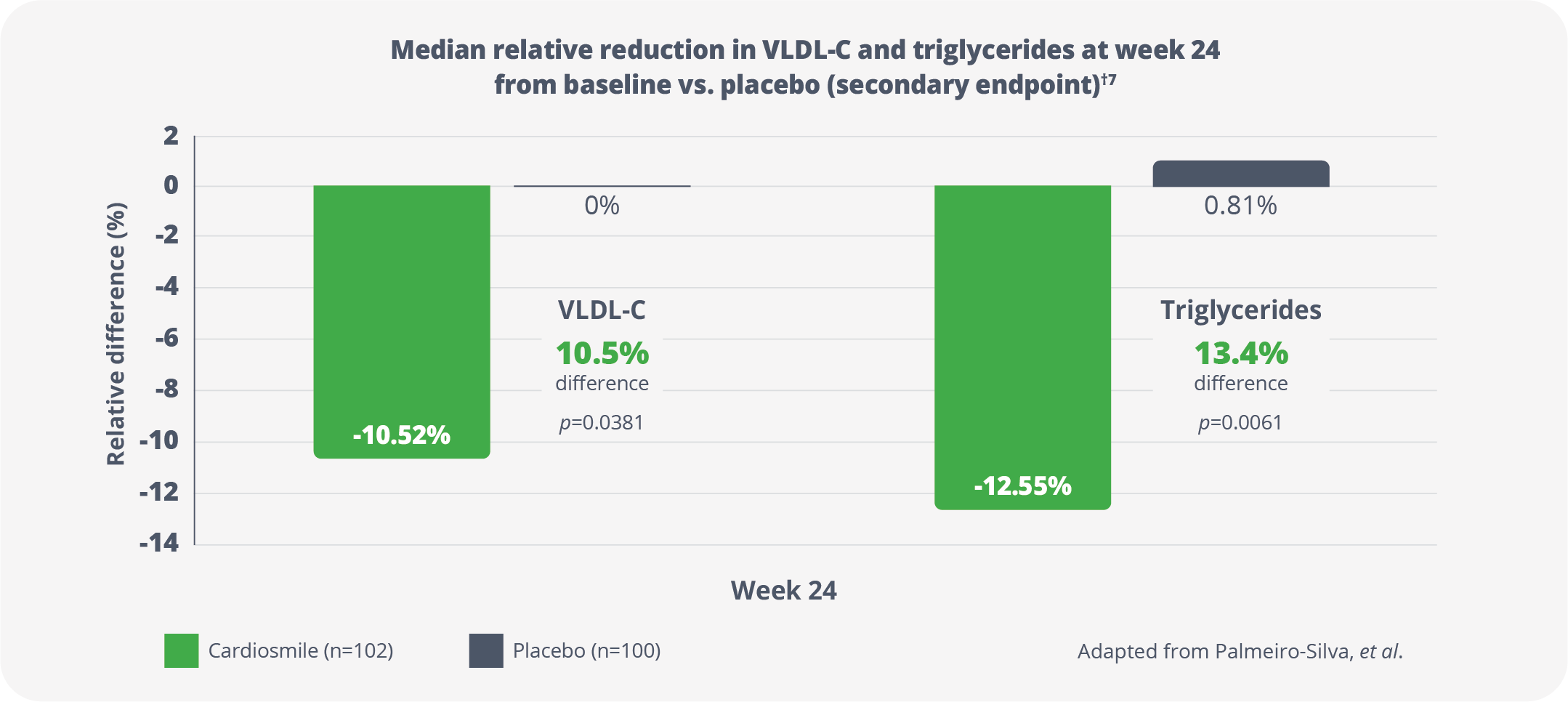
Efficacy results from Palmeiro-Silva, et al.
Effects of daily consumption of an aqueous dispersion of free phytosterol nanoparticles on individuals with metabolic syndrome: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial.
Safety profile in clinical trials:
- Supplementation of Cardiosmile and PS-ester did not adversely influence fat soluble vitamin or carotenoid levels before or after adjustment for LDL-C levels, compared to control.2
- No negative effect on plasma vitamin D levels was observed.2
- At week 24, Cardiosmile demonstrated a 68% improvement in bowel habits (relieving constipation) from visit 1 (p=0.001).2

Health Canada’s assessment of foods containing plant sterols and blood cholesterol lowering
According to guidelines established by Health Canada, plant sterols are considered safe cholesterol-lowering ingredients.3
A Health Canada safety assessment of the addition of plant sterols to foods raised no safety concerns with plant sterol intakes ≤3 g (as free phytosterols) per day in adults and ≤1 g in children.3
Published studies have demonstrated that consuming 3 g of phytosterols/day posed no nutritionalrisk for the general population with respect to beta-carotene.4